When they are first diagnosed, most tumors are restricted to the organ in which they originate and grow only locally. This allows the doctors to plan local treatment to eliminate them. In some cases, however, metastases are already present at the time of the first diagnosis (FIGURES 2 and 3), (WHAT ARE METASTASES?).
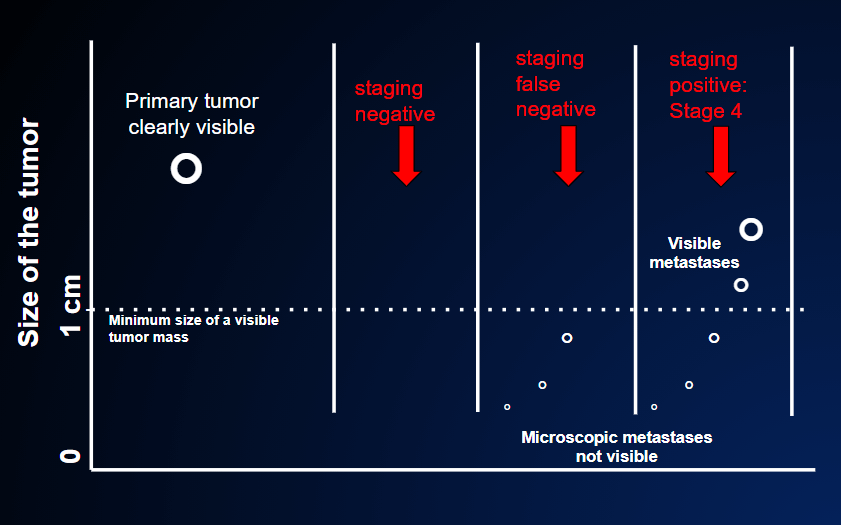
In the second case, the staging result is falsely negative because although the CT, PET scan and magnetic resonance tests are negative (=no tumor in other organs) the primary tumor has already spread outside the local origin, but these small nodules are too small to be revealed by the imaging tests. These tests usually disclose nodules of at least 0.5-1 cm ( the dotted line in the figure). After the primary tumor is removed, the patient is not cured. A relapse will become known when these small nodules have grown above that threshold.
In the third case, the staging result is positive (=presence of cancer in other organs ) because metastases are already seen by the staging tests: they are already large enough at the time the primary cancer is discovered.
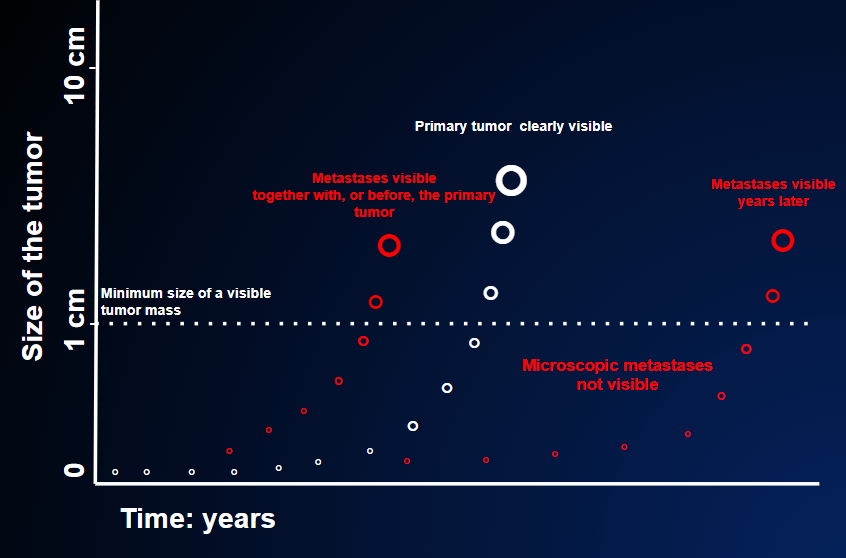
This situation is radically different from the previous one, for two reasons.
- It is much more serious, in that, in the vast majority of cases, the tumor is no longer curable
The treatment strategies are completely different. Indeed, with few exceptions, it is less urgent to begin treatment than in the case of localized tumors, in which prompt treatment does not give the tumor time to metastasize. Here, by contrast, metastases are already present. The aim of treatment is therefore to contain the disease.
Metastatic cancer covers a range of conditions. Some patients may have metastases that are hardly visible and which cause no symptoms; others may have very large metastases that cause great suffering. All these conditions are dealt with in section THERE IS A TUMOR AND THINGS ARE NOT GOING WELL.
